Difference between revisions of "Non-REM 2"
From EEGpedia
(Created page with "* Most common sleep stage during a normal night’s sleep. * Appearance of sleep spindles ** Short burst of waxing and waning rhythmic waves. ** Amplitude of 20-100 microvolt....") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
* Most common sleep stage during a normal night’s sleep. | * Most common sleep stage during a normal night’s sleep. | ||
| − | * Appearance of sleep spindles | + | * Appearance of '''sleep spindles''' |
** Short burst of waxing and waning rhythmic waves. | ** Short burst of waxing and waning rhythmic waves. | ||
** Amplitude of 20-100 microvolt. | ** Amplitude of 20-100 microvolt. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
** Bilateral and synchronous | ** Bilateral and synchronous | ||
** Maximum in the frontal and central regions | ** Maximum in the frontal and central regions | ||
| − | * Appearance of [[K complex]] | + | * Appearance of '''[[K complex]]''' |
| + | * Appearance of <20% '''[[Delta waves]]''' | ||
* All sleep patterns in [[Non-REM 1]] persist in Non-REM 2, except for slow rolling eye movements (SREM). | * All sleep patterns in [[Non-REM 1]] persist in Non-REM 2, except for slow rolling eye movements (SREM). | ||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 3 April 2017
- Most common sleep stage during a normal night’s sleep.
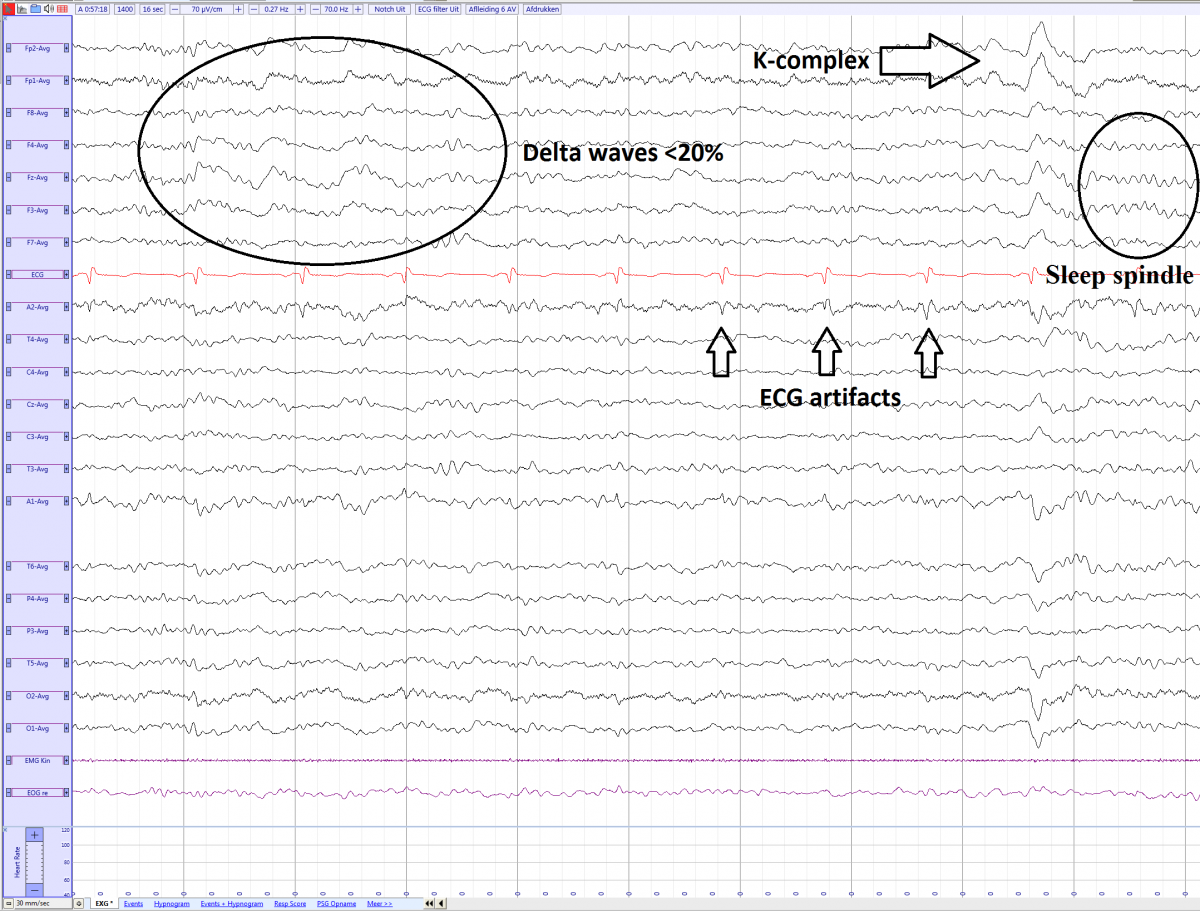
- Appearance of sleep spindles
- Short burst of waxing and waning rhythmic waves.
- Amplitude of 20-100 microvolt.
- Frequency of 12-16 Hz
- The presence of sleep spindles is necessary and sufficient to define non REM 2 sleep
- First appear in infants of 6-8 weeks old
- Bilateral and synchronous
- Maximum in the frontal and central regions
- Appearance of K complex
- Appearance of <20% Delta waves
- All sleep patterns in Non-REM 1 persist in Non-REM 2, except for slow rolling eye movements (SREM).
Non REM 2 sleep with sleepspindles, K-complex and delta waves (average)