Angelman syndrome
From EEGpedia
Background
- In 1/12,000- 1/25,000 children.
- Genetic disorder, loss of function in UBE3A gene on chromosome 15.
- Clinical features apparent after birth, usually within age of 1 or 2 years old.
Clinics
- Delayed psychomotor development.
- In early years often smiling: ‘Happy puppet syndrome’.
- Overeating.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Microcephaly, large tongue and hypersalivation.
- 90% of the patients have seizures ; usually tonic or atone seizures, or absences.
- Vulnerable to infections.
EEG
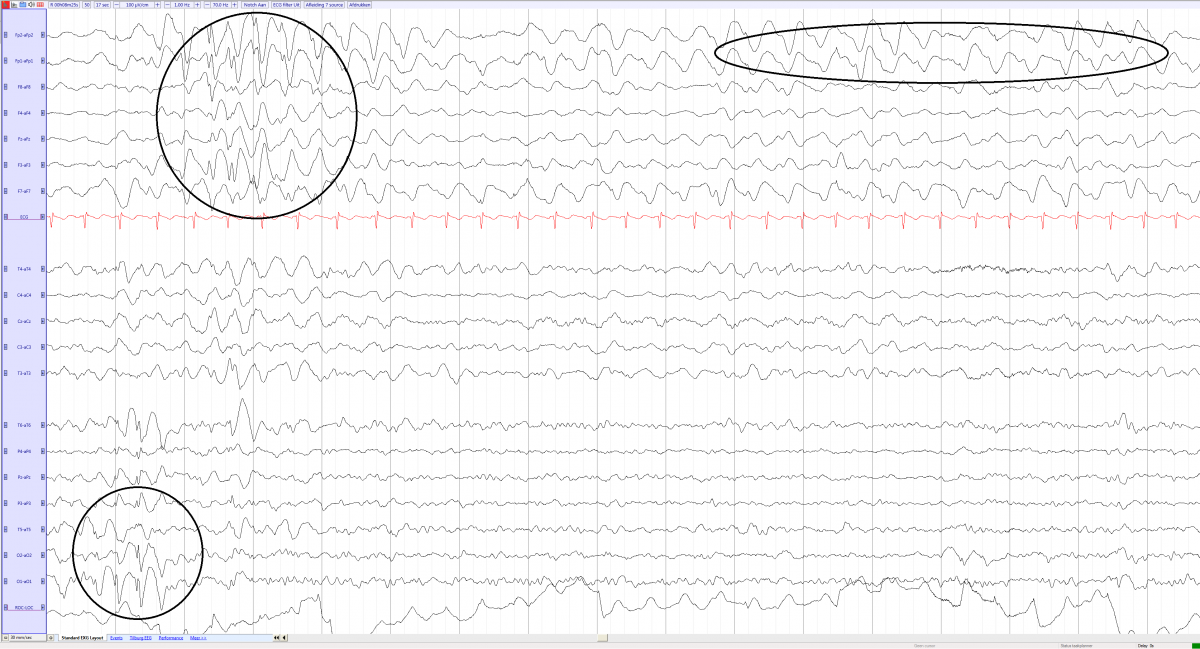
- Frontal slowing
- Rhytmic discharges in 2-4Hz predominently in the frontal and/or occipital regions.
- Occipital discharges can be triggered by closing th eyes.
- EEG similar in patients wit hand without seizures.
Angelman syndrome in an 8-year-old girl (source) with frontal slowing together with occipital and frontal spikes and slow wave complexes, not synchrone