Difference between revisions of "Non-REM 1"
From EEGpedia
(Created page with "* Slow rolling eye movements (SREMs): SREMs are usually the first evidence of drowsiness seen on the EEG. SREMs disappear in stage II and deeper sleep stages. * Decrease of al...") |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 09:13, 3 April 2017
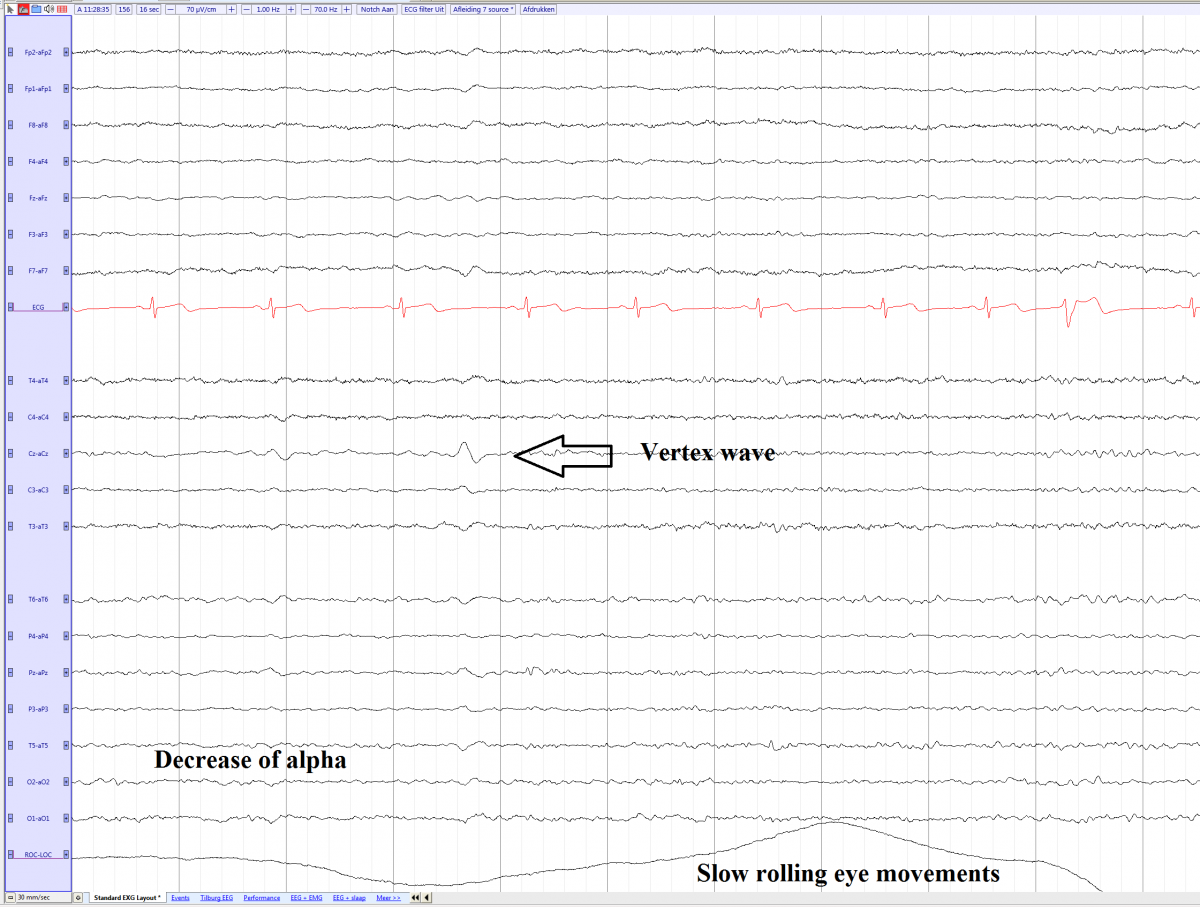
- Slow rolling eye movements (SREMs): SREMs are usually the first evidence of drowsiness seen on the EEG. SREMs disappear in stage II and deeper sleep stages.
- Decrease of alpha rhythm
- Central or frontocentral theta activity
- Enhanced beta activity
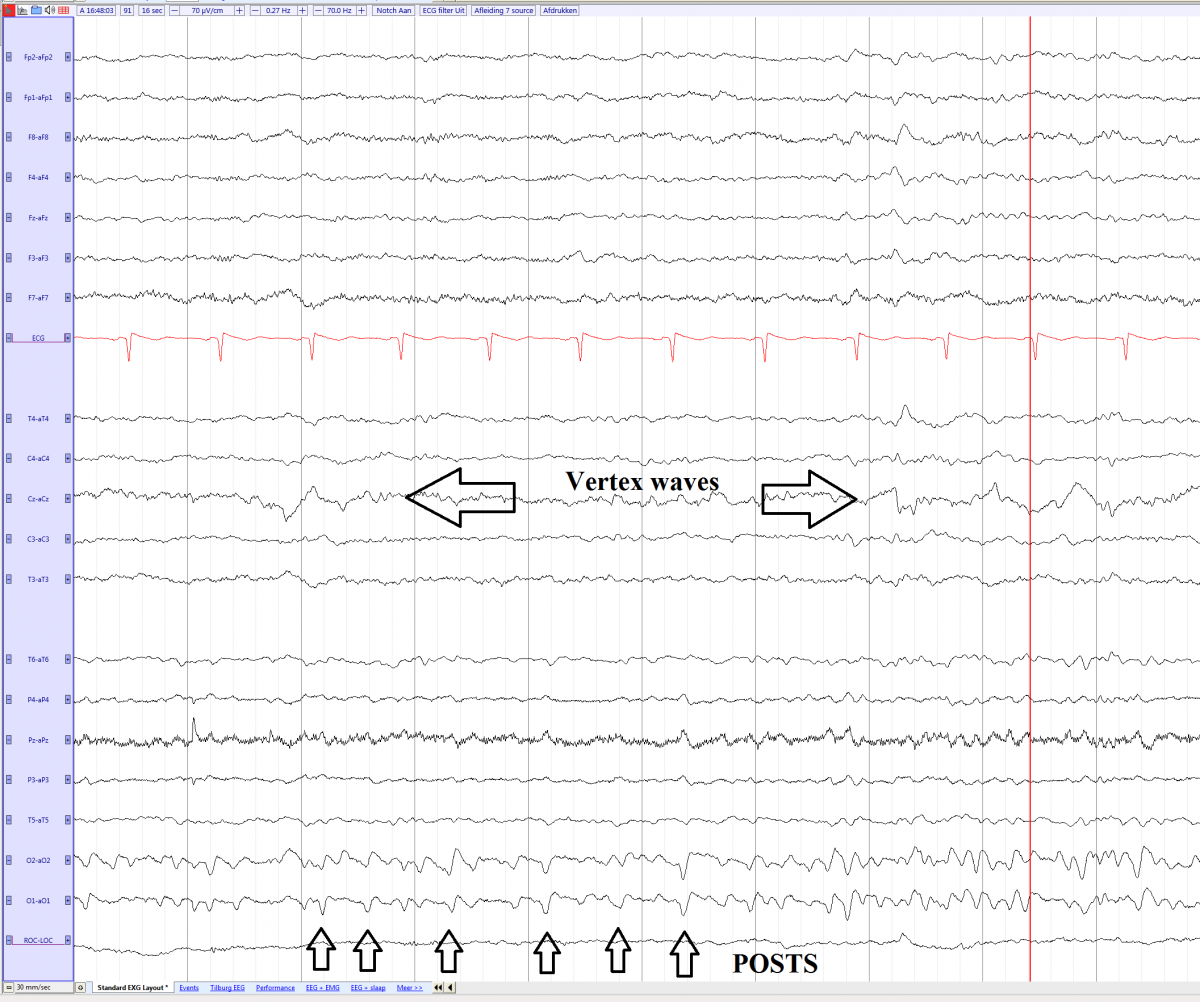
- POSTS (Positive occipital sharp transients of sleep)
- Vertex waves
- Hypnagogic hypersynchrony: Normal variant of drowsiness in children aged 3 months to 13 years. Paroxysmal 3-5 Hz bursts of high-voltage (as high as 350 µV) sinusoidal waves, maximally expressed in the prefrontal-central areas
Non REM 1 sleep with slow rolling eye movements and vertex wave in a young adult (source)
POSTS and vertexwaves in a young female adult in non REM 1 sleep (source)