Difference between revisions of "Panayiotopoulos Syndrome"
From EEGpedia
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* Autonomic dysfunction | * Autonomic dysfunction | ||
** Pale | ** Pale | ||
| − | ** | + | ** Complains of feeling sick and may vomit |
** Sweating | ** Sweating | ||
** Drooling | ** Drooling | ||
Latest revision as of 11:26, 13 July 2017
Background
- Also known as early onset occipital epilepsy
- Common childhood epilepsy syndrome with partial seizures (1 in 8000 children)
- Most common in 2-10 years old, with a maximum around 5 years old
Clinic
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Pale
- Complains of feeling sick and may vomit
- Sweating
- Drooling
- Pupil dilatation or miosis
- Tachy- or bradycardia
- Eye deviation
- Sometimes tonic-clonic movements
- Headache after the seizure
- More than half of the seizures will occur in sleep, particularly in the first hour after falling asleep.
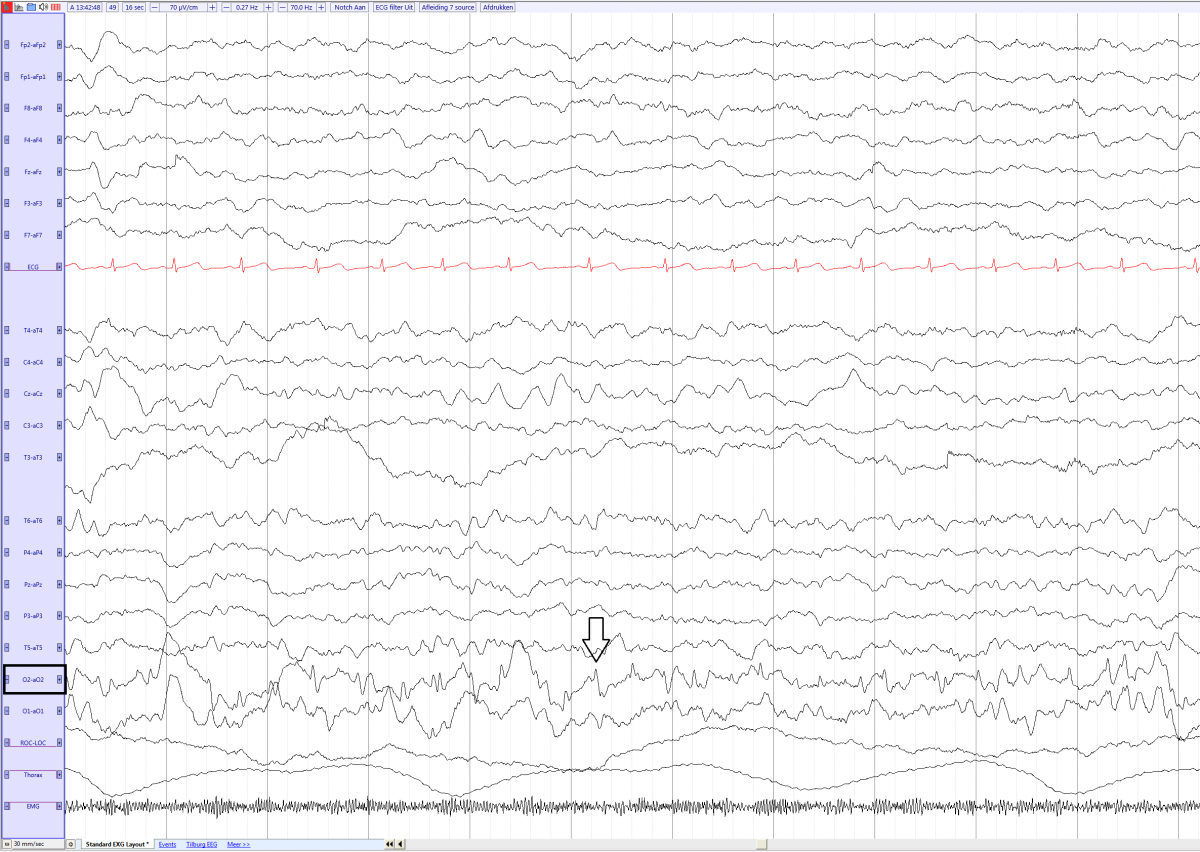
EEG
- Spikes in one or both occipital lobes.
- Sometimes centro-temporal spikes.
- Fixation off sensitivity may be seen: The Spikes are seen when the child’s eyes are closed or if they are not fixating on an object. With eyes opened or fixated, the spikes disappear
- If the EEG done during awake is normal, an EEG during sleep is recommended
Panayiotopoulos Syndrome in a 5 year old girl (source)