Difference between revisions of "Benign Myoclonic Epilepsy in Infancy"
From EEGpedia
(Created page with "==Background== * One of the idiopathic generalized epilepsies * 1% to 2% of epilepsies that start before the age of 3 years * Seizures start between 0.5 and 3 years of age in...") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* Photosensitivity in 20% of the patients | * Photosensitivity in 20% of the patients | ||
* Unexpected acoustic or tactile stimuli can elicit a the myoclonic jerks in 10%. | * Unexpected acoustic or tactile stimuli can elicit a the myoclonic jerks in 10%. | ||
| + | * During sleep in most of the patients the myoclonic seizures persists | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| − | * | + | * Valproic acid was effective in 23 of 30 treated patients <ref>Auvin, S. , Pandit, F. , De Bellecize et al, Benign Myoclonic Epilepsy in Infants: Electroclinical Features and Long‐term Follow‐up of 34 Patients. Epilepsia, 2006 47: 387-393. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00433.x</ref> |
* Patients with acoustic and somatosensory evoked myoclonic seizures may not need treatment. | * Patients with acoustic and somatosensory evoked myoclonic seizures may not need treatment. | ||
==EEG== | ==EEG== | ||
| − | * '''Inter-ictal''': | + | * '''Inter-ictal''': Usually normal, sometimes generalized [[Spike slow wave complex]] or [[Polyspikes slow wave complex]] |
* '''Ictal''': Brief generalized [[Spike slow wave complex]] or [[Polyspikes slow wave complex]] | * '''Ictal''': Brief generalized [[Spike slow wave complex]] or [[Polyspikes slow wave complex]] | ||
| − | |||
* Sometimes photosensitivity | * Sometimes photosensitivity | ||
* Normal background rhythm | * Normal background rhythm | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
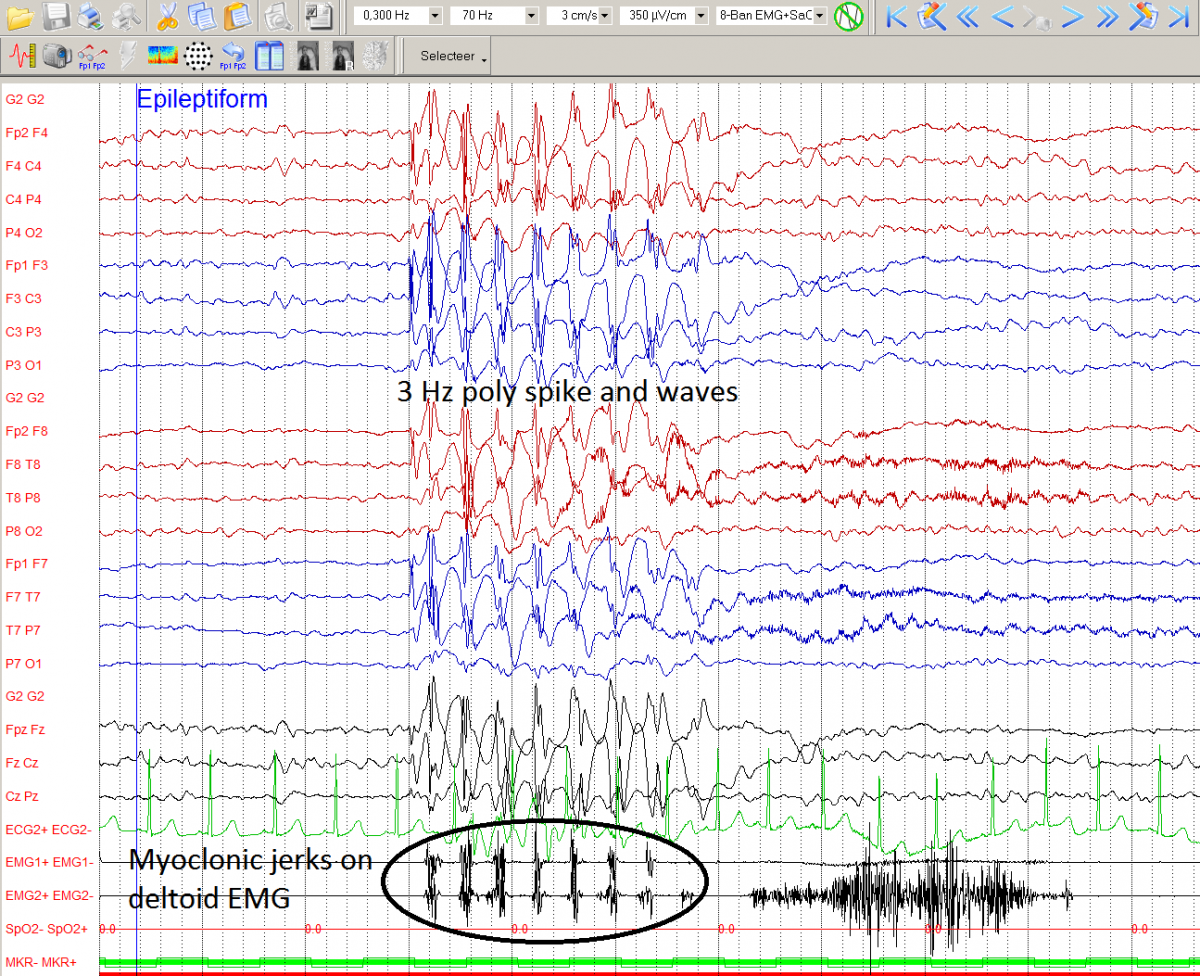
| − | ''''' | + | '''''5 year old girl with 3 Hz generelized polyspike waves and myoclonic jerks (double banana and EMG on deltoid muscle)''''' |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:5_year_old_girl_with_3_Hz_generelized_polyspike_waves_and_myoclonic_jerks_(double_banana_and_EMG_on_deltoid_muscle)_EEGpedia.png|border|none|1200px|left]] |
Latest revision as of 22:52, 8 June 2018
Contents
Background
- One of the idiopathic generalized epilepsies
- 1% to 2% of epilepsies that start before the age of 3 years
- Seizures start between 0.5 and 3 years of age in developmentally normal children. However, some cases have a later onset up to 4 years
- A family history of febrile seizures and epilepsy is often reported
- Remission usually occurs within 1 year (6 months to 5 years) from onset.
- The outcome is generally benign. In rare cases, myoclonic epilepsy such as Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy may follow Benign Myoclonic Epilepsy in Infancy
Clinic
- Myoclonic jerks involving mostly the upper part of the body, singular or clusters
- Consciousness is normally intact
- Photosensitivity in 20% of the patients
- Unexpected acoustic or tactile stimuli can elicit a the myoclonic jerks in 10%.
- During sleep in most of the patients the myoclonic seizures persists
Treatment
- Valproic acid was effective in 23 of 30 treated patients [1]
- Patients with acoustic and somatosensory evoked myoclonic seizures may not need treatment.
EEG
- Inter-ictal: Usually normal, sometimes generalized Spike slow wave complex or Polyspikes slow wave complex
- Ictal: Brief generalized Spike slow wave complex or Polyspikes slow wave complex
- Sometimes photosensitivity
- Normal background rhythm
- Electromyogram show one or repetitive myoclonia
5 year old girl with 3 Hz generelized polyspike waves and myoclonic jerks (double banana and EMG on deltoid muscle)
Notes
- ↑ Auvin, S. , Pandit, F. , De Bellecize et al, Benign Myoclonic Epilepsy in Infants: Electroclinical Features and Long‐term Follow‐up of 34 Patients. Epilepsia, 2006 47: 387-393. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00433.x