Difference between revisions of "Childhood Absence Epilepsy"
From EEGpedia
(Created page with "'''Childhood Absence Epilepsy (CAE)''' =Background= * Usually in children between 3 and 10 years old * Most around 5-6 years old when the first absence seizure was seen * 1...") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ==Background== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | =Background= | + | |
* Usually in children between 3 and 10 years old | * Usually in children between 3 and 10 years old | ||
* Most around 5-6 years old when the first absence seizure was seen | * Most around 5-6 years old when the first absence seizure was seen | ||
* 1 in 15.000-50.000 children | * 1 in 15.000-50.000 children | ||
| − | * Siblings of children with Childhood Absence Epilepsy have about a 1 in 10 chance of developing epilepsy. | + | * Siblings of children with Childhood Absence Epilepsy (CAE) have about a 1 in 10 chance of developing epilepsy. |
| − | =Clinic= | + | ==Clinic== |
* Staring spells during which the child is not aware or responsive | * Staring spells during which the child is not aware or responsive | ||
* Eyes may roll up briefly or the eyes may blink. | * Eyes may roll up briefly or the eyes may blink. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 15: | ||
| − | =EEG= | + | ==EEG== |
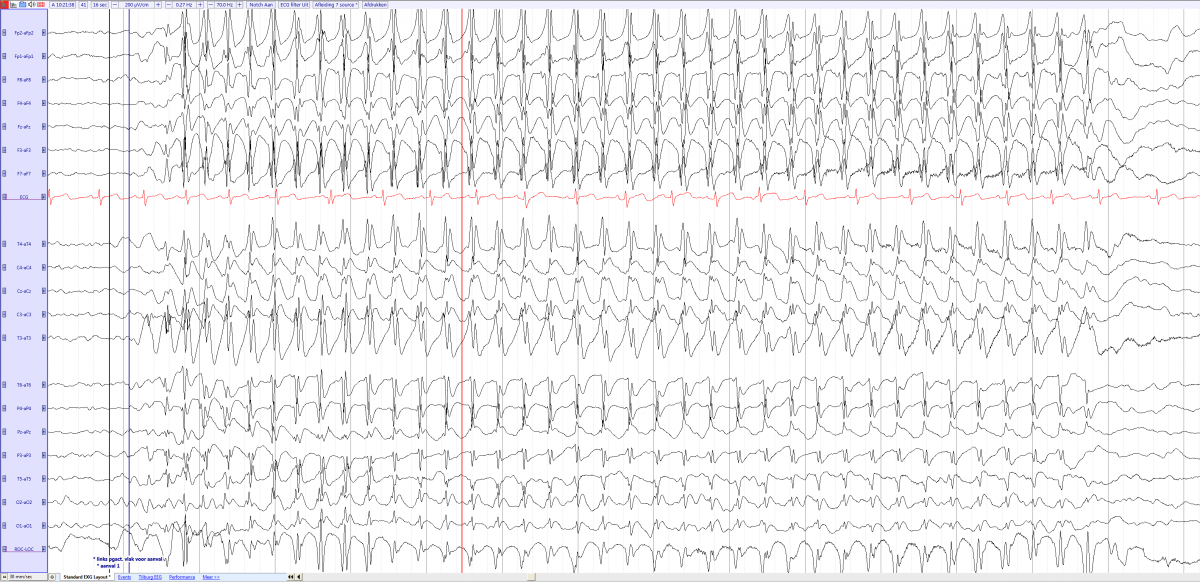
| − | * Generalized [[Spike slow wave complex]] of 3 Hz | + | * '''Inter-ictal:''' Normal posterior rhythm, though with frequent rhythmic posterior delta activity |
| − | * Hyperventilation triggers an absence seizure in over 80% of children with | + | * '''Ictal:''' Generalized [[Spike slow wave complex]] of 3 Hz |
| + | * Hyperventilation triggers an absence seizure in over 80% of children with Childhood Absence Epilepsy. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:19, 8 June 2018
Background
- Usually in children between 3 and 10 years old
- Most around 5-6 years old when the first absence seizure was seen
- 1 in 15.000-50.000 children
- Siblings of children with Childhood Absence Epilepsy (CAE) have about a 1 in 10 chance of developing epilepsy.
Clinic
- Staring spells during which the child is not aware or responsive
- Eyes may roll up briefly or the eyes may blink.
- Sometimes repetitive movements like mouth chewing.
- Usually the absence last for around 10 seconds and ends abruptly
- After the seizure the child resumes normal activity
- Could be provoked by hyperventilation
EEG
- Inter-ictal: Normal posterior rhythm, though with frequent rhythmic posterior delta activity
- Ictal: Generalized Spike slow wave complex of 3 Hz
- Hyperventilation triggers an absence seizure in over 80% of children with Childhood Absence Epilepsy.
Childhood absence epilepsy in a 4,5 year old girl, with typical generalized 3 Hz spike wave complexes (source)