Difference between revisions of "SIRPID (Stimulus Induced Rhythmic, Periodic, or Ictal Discharges)"
From EEGpedia
(Created page with "==Background== * Stimulus Induced Rhythmic, Periodic, or Ictal Discharges (SIRPID) * Due to cortical and subcortical brain damage (thalamo-cortical dysfunction) * Often seen a...") |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
* Often seen after acute brain injury (around 75%) | * Often seen after acute brain injury (around 75%) | ||
* Discharges are induced by a tactile stimulus, i.e. touch or pain. | * Discharges are induced by a tactile stimulus, i.e. touch or pain. | ||
| − | |||
==Clinic== | ==Clinic== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 9: | ||
* 50% has (sub)clinical seizures. | * 50% has (sub)clinical seizures. | ||
* Risk factor for development of status epilepticus. | * Risk factor for development of status epilepticus. | ||
| − | |||
==EEG== | ==EEG== | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 17 January 2018
Background
- Stimulus Induced Rhythmic, Periodic, or Ictal Discharges (SIRPID)
- Due to cortical and subcortical brain damage (thalamo-cortical dysfunction)
- Often seen after acute brain injury (around 75%)
- Discharges are induced by a tactile stimulus, i.e. touch or pain.
Clinic
- In critically ill patients
- 50% has (sub)clinical seizures.
- Risk factor for development of status epilepticus.
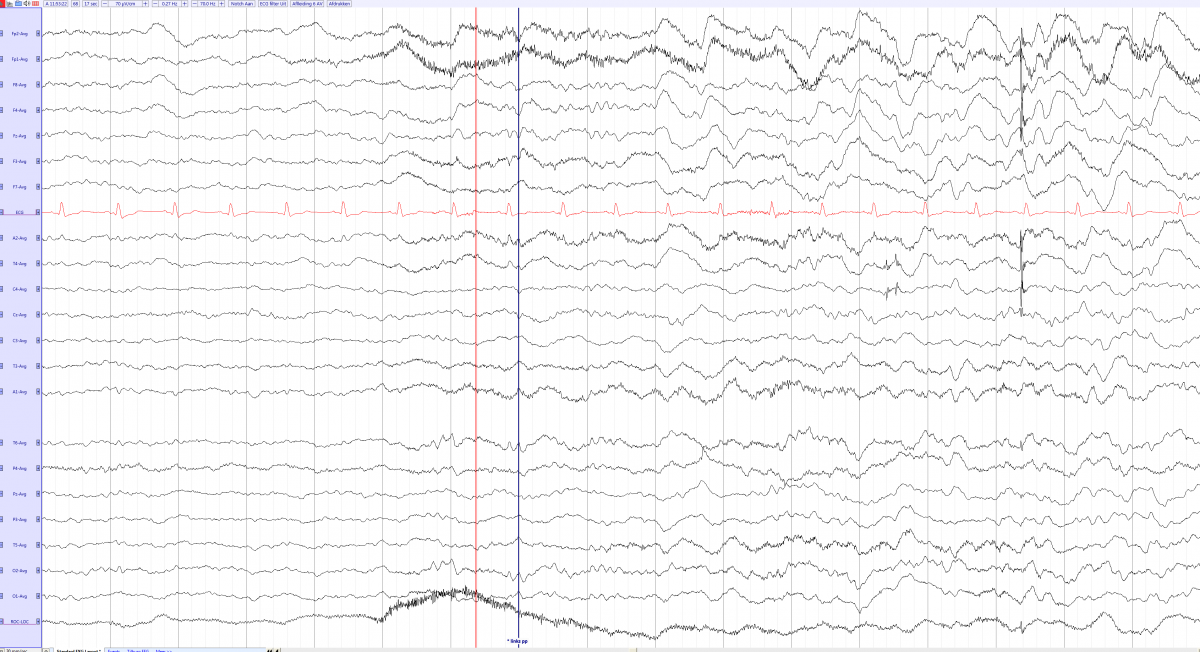
EEG
- Encephalopatic background EEG
- Rhythmic delta discharges after a stimulus, i.e. pain.
- Generalized or focal discharges.
- Lasting seconds to hours
Generalized SIRPIDs after pain stimulus (blue line) (Average)