Difference between revisions of "6 Hz spike-and-wave bursts (WHAM and FOLD)"
From EEGpedia
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
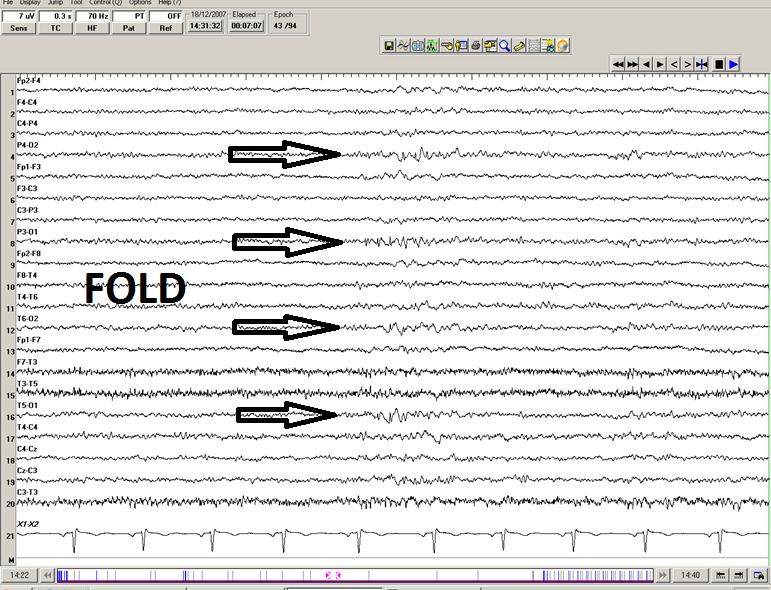
''''' FOLD: low amplitude, bilateral occipital, synchronous spike and waves (double banana)''''' | ''''' FOLD: low amplitude, bilateral occipital, synchronous spike and waves (double banana)''''' | ||
| + | |||
[[File: FOLDs_(double_banana).png|border|1200px]] | [[File: FOLDs_(double_banana).png|border|1200px]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
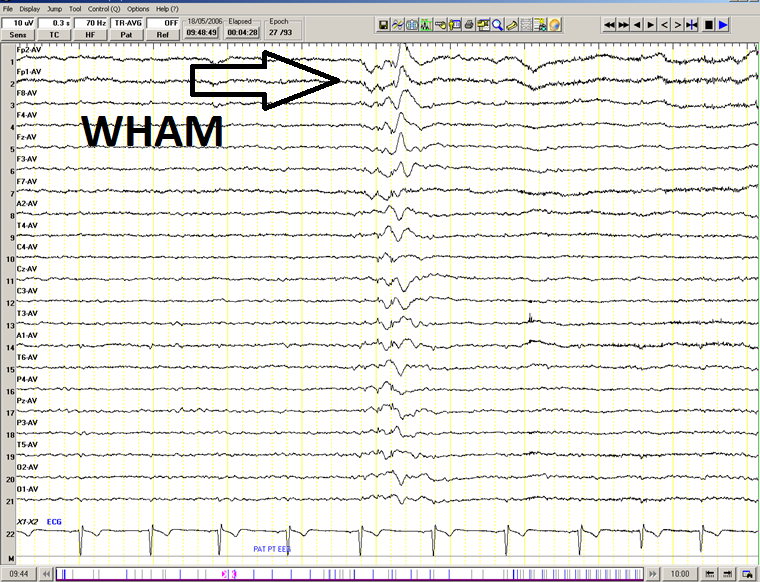
''''' WHAM: anterior, bilateral, high amplitude spike and wave, associated with epilepsy (average)''''' | ''''' WHAM: anterior, bilateral, high amplitude spike and wave, associated with epilepsy (average)''''' | ||
| + | |||
[[File: WHAM_(average)_1.png|border|1200px|left]] | [[File: WHAM_(average)_1.png|border|1200px|left]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 16:21, 28 June 2018
6 Hz spike-and-wave bursts (WHAM and FOLD)
Synonymes: Phantom spike and waves
- Brief bursts of low amplitude spike-and-slow wave 6Hz (5-7Hz)
- Spike often not clearly discernible: “phantom”
- Bilateral and synchronous
- Maximal at midline (posterior or anterior)
- Relaxed wakefulness and drowsiness
- Adolescents and young adults
- duration of 1-2 seconds
Two subtypes of 6 Hz spike-and-wave bursts
- WHAM: Waking, High amplitude spike (>45uV), Anterior, Male
- Associated with epilepsy especially when high amplitude spikes, rate <5-6Hz and persists during deep sleep
- FOLD: Female, Occipital, Low amplitude spike, Drowsy
- Not associated with epilepsy
FOLD: low amplitude, bilateral occipital, synchronous spike and waves (double banana)
WHAM: anterior, bilateral, high amplitude spike and wave, associated with epilepsy (average)